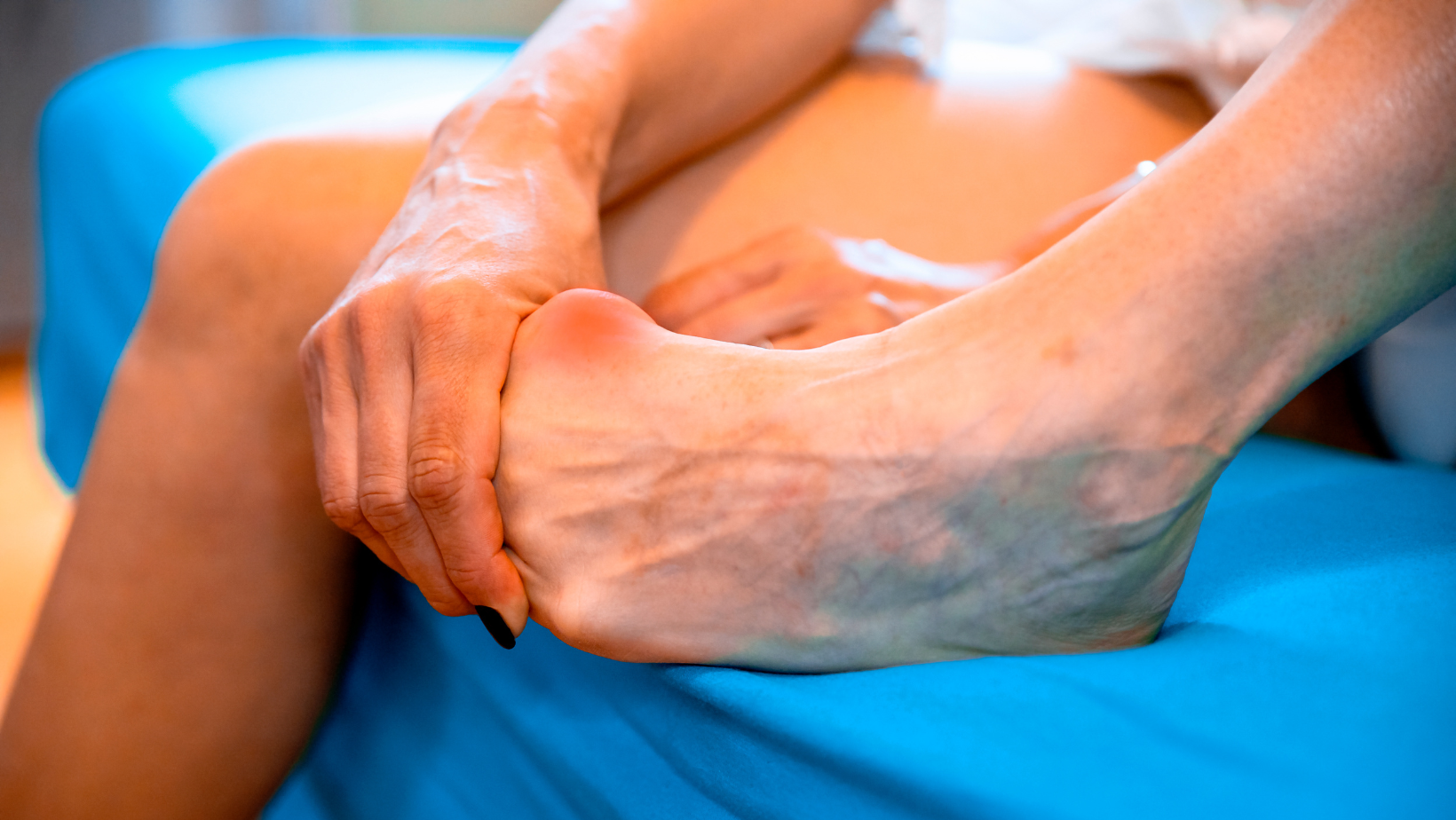
Bunions are a common foot condition that can cause pain and discomfort. They are characterized by a bony bump that forms at the base of the big toe. While bunions are often associated with wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes, there are various factors that contribute to their development. In this article, we will explore the causes of bunions and provide valuable insights from a podiatrist to help you understand this condition better.
1. Foot Structure and Inherited Factors
- Deviated Bone Structure: Some individuals have an inherited foot structure that predisposes them to develop bunions. This can include a foot shape with a prominent first metatarsal bone, which can cause the big toe to deviate inward.
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic factors can make a person more susceptible to developing bunions. If you have a family history of bunions, you may have an increased risk of developing them as well.
2. Improper Foot Mechanics and Overpronation
- Imbalance in Foot Mechanics: Abnormal foot mechanics, such as overpronation (excessive inward rolling of the foot), can contribute to the development of bunions. Overpronation can put excessive stress on the big toe joint, leading to bunion formation.
- Flat Feet: Individuals with flat feet often experience overpronation, which can increase the risk of developing bunions. Flat feet can cause the foot to become unstable and lead to improper weight distribution.
3. Wearing Tight or Inappropriate Footwear
- Narrow or Pointed Shoes: Wearing tight or narrow shoes that squeeze the toes together can put pressure on the big toe joint and lead to bunion formation. High-heeled shoes, especially those with a pointed-toe box, can exacerbate the problem by pushing the toes forward and increasing the pressure on the joint.
- Improper Shoe Fit: Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate space and support for the toes can contribute to the development of bunions. It is important to choose shoes with a wide toe box and proper arch support to help prevent bunions.
4. Trauma or Injury
- Foot Trauma: A previous foot injury or trauma to the big toe joint can increase the likelihood of developing a bunion. The joint may become weakened or damaged, leading to an abnormal alignment of the toe.
- Repetitive Stress: Engaging in activities that place repetitive stress on the foot, such as ballet dancing or certain sports, can contribute to bunion development. The constant pressure and strain on the big toe joint can gradually cause the joint to deform.
5. Aging and Hormonal Factors
- Aging: As we age, the ligaments and tendons in our feet can become weaker and less supportive. This can contribute to the development of bunions over time.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes, particularly in women, may play a role in the development of bunions. Hormones can affect the elasticity of ligaments and tendons, potentially leading to joint instability and bunion formation.
Conclusion
Bunions are a complex foot condition influenced by a combination of factors. While tight shoes are often blamed for bunions, it is important to recognize that various genetic, structural, and lifestyle factors can contribute to their development. If you are experiencing bunion symptoms or are concerned about your foot health, consulting a podiatrist is recommended. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation, offer treatment options, and provide guidance on proper footwear and preventive measures to help manage and alleviate bunion-related discomfort. Call us today at 833-433-7227 or visit our website to book an appointment. We look forward to welcoming you into our warm, caring environment and helping you take control of your foot health.